Although 80% of organizations have now prioritized third-party risk management, almost half (43%) of respondents from a recent Panorays survey indicate they are lacking this visibility into their supply chain. Rapid adoption of cloud migration and remote work are responsible for employees’ increasing reliance on unapproved devices and software, introducing third and Nth party risk. Gartner estimates that as much as 30% – 40% of IT budgets are spent on Shadow IT; other experts believe that estimate is conservative.
How can your organization proactively identify whether or not your third parties – or any other part of your supply chain – is using these applications, services or systems? You’ll need to establish a system for evaluating fourth-party risk.
What is a Fourth-Party Risk?
A fourth-party risk is any risk posed to your organization by the vendors and suppliers of your third parties. Just as organizations contract work out to third parties, so too do their third parties, who subcontract work out to fourth parties. These critical fourth parties pose cybersecurity risks, operational risks, or other potential risks – risks that are particularly challenging to mitigate because fourth parties are often unknown to the organization and aren’t bound to the same service level agreements (SLAs) or regulatory requirements as third parties. To mitigate these risks, an important part of third-party risk management is being able to identify and evaluate fourth-party security risks, ranking each based on the most critical vendors.
The most important risk factor in fourth-party risk is concentration risk. Concentration risk identifies all of your third-party interactions and the fourth-party relationships that are most frequently used by your supply chain. For example, if all of your vendors are using AWS, AWS is considered a risk factor for your organization, since if AWS is experiencing downtime for any reason, your organization will probably also be down. Another example is if your fourth parties all share a common vulnerability that might cause disruption. Not only do these fourth parties expose third parties to risk, but they can also expose your organization to a data breach, leak your company’s sensitive data or pose additional security risks.
How Secure are Your Third-Party and Fourth-Party Vendors?
Panorays is focused on third-party security management: the security posture of suppliers, vendors, partners and others doing business with an organization.
In an assessment of thousands of companies, Panorays found that there is a direct correlation between the security posture of the third party and its fourth parties.
Each third-party organization relies on dozens, if not hundreds, of additional fourth parties. In our research, we mapped myriads of connections between third and fourth parties, including their cyber posture ratings, to understand whether any correlation exists.
Revealing and Collecting Information about Third and Fourth Parties
During the cyber posture assessment of a company, Panorays automatically discovers all of the company’s digital assets, including domains and IP addresses. Panorays then collects information about each asset; for example, the technologies that are in use. The data collection includes common methods such as technology fingerprinting and DNS record mining.
Since Panorays has a large database of hundreds of thousands of companies, it can correlate the external assets to real companies and automatically detect many suppliers. Many times, these are suppliers that the organization itself is not even aware it is using.
While there is an obvious bias towards technology suppliers, Panorays has additional methods for identifying non-tech suppliers in the discovery process.
Portraying an Accurate View of Suppliers Connected to Third Parties
Panorays collected data from 37,000 fourth parties, generated by over 2,000 third parties. The research showed that there are a handful of fourth parties that are connected to a very high percentage of third parties.
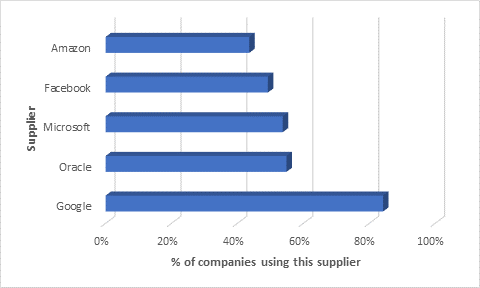
Over 84% of inspected third parties used Google as a fourth party. These include Google Cloud Platform for infrastructure, Google Maps app integration, Google Analytics and so on.
It is not surprising that Microsoft or Google have such a high reach; therefore, a significant security incident involving one of these companies could impact millions of organizations worldwide.
We removed these suppliers from our dataset to get a more precise view of the unique suppliers each company is using.
Assessing Supplier Portfolio Cyber Posture
For each third party, we built a supplier portfolio and ran an assessment of each fourth party to generate its cyber posture rating. The fourth-party rating is a mean of the cyber posture rating of all the fourth parties. In addition, we assessed the cyber posture of the third parties themselves.
For example:
We checked the correlation between this cyber posture rating and the fourth-party rating.
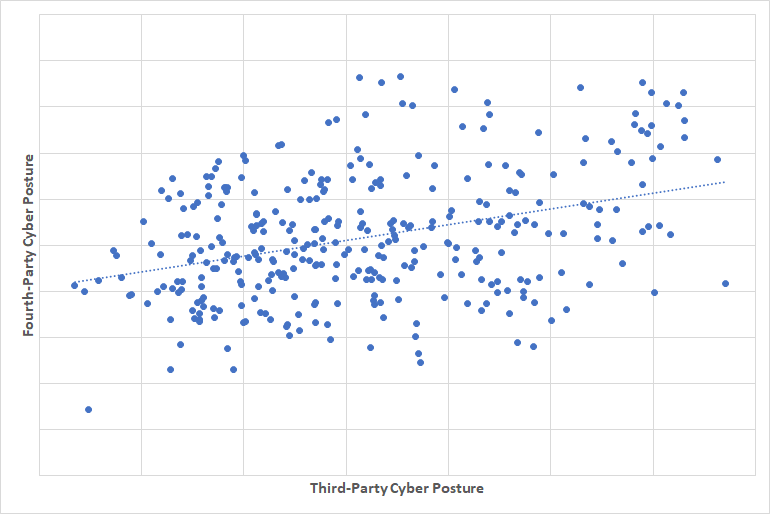
We can see a clear correlation that third parties with a high cyber posture rating have a high fourth-party rating as well.
Seen in a different way, we grouped the cyber posture ratings into five levels to see the chances of receiving a good supplier rating, which would be above 80.
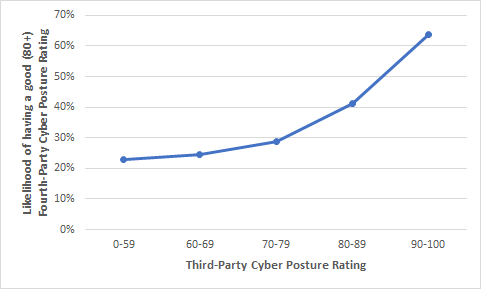
Here we see that third parties with a cyber posture rating of between 90 to 100 have a 63% chance that their fourth parties will have a cyber posture rating of at least 80. On the whole, we see that as third parties’ cyber posture ratings increase, their chances of doing business with fourth parties that have good cyber postures increase as well.
To sum up our study, we found that organizations who take their third parties’ cyber posture seriously, take steps to remediate any security gaps and only partner with companies with high cyber posture scores are also likely to take their own cyber posture seriously.
The Connection Between Third-Party Risk Management and Fourth Parties
In this research, we found that third parties with a high cyber posture score will have fourth parties with a high cyber posture as well.
There are a number of evident reasons for this, such as:
- Higher security awareness
- In-place supplier management programs
- Bigger budgets for more established suppliers
- Choosing a supplier with similar standards and culture
Clearly, both third-party security management and fourth-party risk management are integral components of companies’ cyber posture, and the numbers in this research bear this out. This is one more reason for managing third-party suppliers’ security state and working with vendors that have security awareness and controls in place.
Mastering Fourth-Party Risk Management with Panorays
Fourth parties that are part of your extended digital supply chain pose a risk to your organization not only in the case of disruption of services but also the possibility of exposing sensitive data and information. Panorays allows you to assess your organization’s risk exposure deeply and widely, giving you a clear view of your extended digital supply chain. This enables your organization to more effectively defend against supply chain attacks and other security threats.
Its latest features include:
- Supply Chain Discovery. Map out relationships between your third parties and their vendors. Gain insight into how risk events might impact you through third, fourth and Nth-party suppliers.
- Risk Insights and Response Portal. Get alerts for all third-party breaches and vulnerabilities on third-party breaches across their entire supply chain. Armed with this information, you’ll be able to proactively defend against cyber risks by either sending incidence response questionnaires to relevant direct and indirect suppliers, conducting continuous cyber assessments, or both.
See how Panorays gives you visibility and control over your digital supply chain with Extended Attack Surface Montioring.
FAQs
A fourth-party risk is a risk posed to your organization from a business relationship a third party has with its vendor. For example, if your third party uses a supplier that has suddenly gone out of business, that business disruption poses an operational risk to your organization.
An example of a fourth-party risk is if your company outsources a vendor that uses the MOVEIt file transfer application. In June, the MOVEIt application announced a zero-day vulnerability, posing a risk to the third-party vendor your company has outsourced, and by extension, a fourth-party risk to your company as well.
The difference between a third-party vendor and a fourth-party vendor is where the vendor sits in your supply chain. A third-party vendor is a direct supplier, partner, external contractor or third party that your organization relies on or has a business relationship with. In contrast, a fourth party is an indirect vendor such as a partner, supplier, external contractor or other vendor of your third party. Third-party vendor risk is also easier to identify, mitigate and remediate than fourth-party risk. Fourth-party risks are difficult to assess and identify since they are unknown to your organization and not included in the Service-Level Agreements (SLAs) your organization has with its third parties.






