IT asset management has become more challenging today due to many factors, including increased migration to the cloud, more complex IT environments, the need to both improve employee experience and productivity, as well as a trend toward an increase in software audits. (And that’s a partial list). As a result, more organizations are investing in their IT asset management. According to a recent report from Deloitte, the primary drivers for investment in IT asset management include cost optimization (83%); reduction of financial costs and risks posed by audits (60%); and compliance with regulations (50%).
So what exactly is IT asset management, what benefit does it deliver organizations, and how can it help you manage third-party risk?
What is IT Asset Management?
IT asset management (ITAM) is the process of tracking and managing the items in your IT infrastructure throughout the vendor lifecycle, from onboarding to offboarding. It is important because proper IT asset management delivers greater visibility into your IT assets, enabling you to operate more efficiently, meet compliance and regulations, mitigate cybersecurity threats, and ensure business continuity in the event of an attack, and effectively budget and forecast expenses. It is also an essential component of third-party risk management.
The 3 Main Types of IT Asset Management
IT asset management can be categorized into several main classifications, based on the type of asset: hardware, software, and information.
Hardware Asset Management
Hardware asset management refers to the physical assets of an organization. For example, critical services such as healthcare organizations must be able to accurately manage their hardware in real-time to know how many monitors, X-rays, and MRI machines it has available at any point on their facilities and any nearby branches it works with to ensure operational efficiency. In the event of a security incident, efficient hardware asset management allows it to reroute patients who need to use these specific services to those available and located nearby.
Software as a Service (SaaS) Asset Management
Software as a Service (SaaS) asset management refers to any software integrated into an organization’s infrastructure or outsourced to a third, fourth, or even fifth party. It involves managing software licenses, vulnerability and patch management, and monitoring the use of underutilized assets to reduce operational costs. All of these have implications for third-party risk. For example, a financial institution must secure its payment data and ensure any third party using the data (e.g. CRM or payment processor) meets the relevant compliance and regulations and maintains its license to continue using these third parties.
Information Asset Management
Information asset management is critical for securing sensitive data shared with third parties, meeting compliance, and managing third-party risk. For example, healthcare organizations need to ensure that both they and the third parties they do business with meet HIPAA compliance and other data protection requirements, such as encryption and access control.
What is an IT Asset?
An IT asset is software, hardware, or information resource that a company relies on to support its IT infrastructure. This table lists different examples of IT assets according to each of these categories.
| Software | Hardware | Information |
| Operating system (Windows, Mac, Linux) | Servers | Software licenses |
| Office Suites (Microsoft Office, Google Workspace) | Routers and switches | Personally identifiable information (PII) |
| SQL server | Desktops, laptops, tablets | Patents |
| Antivirus programs | Printers | Performance reviews |
| Encryption tools | External hard drives | Audit reports |
| Salesforce, Hubspot, CMS | Storage area network (SAN) or Network Attached Storage (NAS) | Data, analytics and insights |
Why is IT Asset Management Important for Third Party Risk?
One of the additional reasons IT asset management today is more complex than it once was is because organizations often turn to third parties to provide them IT services. Many times, these third parties then turn to fourth parties to manage aspects of these same services. This increases the complexity of the supply chain and the risk of vulnerabilities and weaknesses that can potentially harm your business.
Proper IT asset management addresses these needs by enabling companies to identify and track assets along their entire supply chain (e.g., third, fourth and n-th parties). This makes it easier for them to assure business continuity in the event of a data breach or security incident, improve incident response time, and mitigate risks all while helping to track and minimize operational costs.
Objectives of the ITAM Process
When you know exactly what software, hardware and information your organization has, it’s much easier to manage your IT infrastructure and respond in the event of a data breach or security incident while at the same time tracking and optimizing operational costs.
Other benefits include:
- Incident management. IT asset management enables organizations to understand the origin of incidents. For example, if a patient sends a ticket complaining that the patient portal they are using keeps crashing, proper asset management can determine that the patient needs more free space on their computer.
- Problem management. IT asset management enables organizations to detect problems in the IT infrastructure, such as bugs in the newly updated software, and find solutions (e.g., reverting to an older version of the software).
- Change management. IT asset management enables organizations to make changes in the IT infrastructure more efficiently, with minimal downtime and impact.
The ISO standards for IT Asset Management
The ISO 55000-550002 is a set of standards developed by the ISO Technical Committee 251 (ISO/TC 251) that provides internationally recognized guidelines for IT asset management. Executive and security teams in organizations across industries use them to implement a new IT asset management or maintain or improve a current one. As an internationally accepted standard, it gives organizations confidence that they have an effective and proven strategy for their IT asset management.
IT Asset Management Best Practices
As asset management evolved to include not only assets within an organization but those it shared with third parties, organizations have turned to asset management solutions to ensure their company is effectively following best practices.
IT Asset Inventory
Tracking and discovering assets is the first step of IT asset management. As businesses increasingly rely on third, fourth, and even fifth parties as service providers, it has become more difficult to track and manage assets. For example, a financial company may have a relationship with a data storage company (e.g. third party) to store its personally identifiable information (PII) data. That data storage company may then outsource its data storage to a cloud storage company such as Google or Amazon (e.g. fourth party).
IT Asset Tracking
For smaller or medium-sized companies, IT assets may be tracked in spreadsheets (e.g. an HR head tracking the hardware assets of each employee for hybrid work environments), but for larger companies, this may be insufficient. After assets are discovered and inventory is taken, they need to be managed through the vendor lifecycle. Many advanced IT asset management solutions leverage AI to detect assets across the supply chain.
IT Asset Maintenance: The 5 Stages of the IT Asset Lifecycle
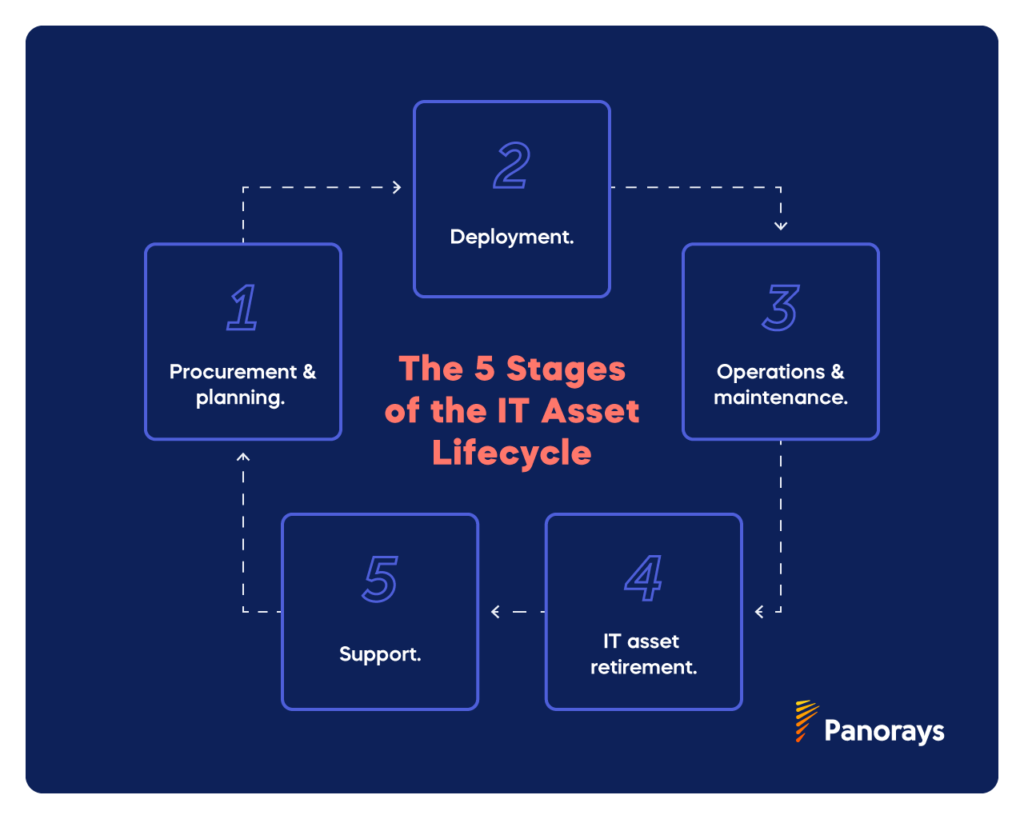
IT asset management must be maintained throughout the lifecycle of the IT asset, including:
- Procurement and planning. This stage includes budgeting, forecasting, and cost-benefit analysis of different IT assets.
- Deployment. This involves setting up, configuring, installing, and training users on how to use the different IT assets to ensure optimal performance.
- Operations and maintenance. Maintaining and monitoring IT assets to ensure they are being used correctly and so that any issues can be identified as quickly as possible.
- Support. This stage includes providing support to users as assets age through helpdesks and technical support.
- IT asset retirement. At a certain point, IT assets no longer deliver value to users and need to be correctly disposed of, ensuring that any sensitive data is erased.
Continuous IT Asset Monitoring and Identification
Due to the dynamic nature of both IT infrastructure environments and third-party business relationships, IT asset management must be monitored continuously. New equipment is constantly purchased, upgrades are made, licenses are renewed, employees leave the organization with their assets now unassigned. Organizations change suppliers, suppliers merge, etc. All of these changes need to be tracked and managed. Many IT asset management software deliver automatic monitoring and identification of IT assets continuously with customized reports to let organizations know the status of all of their IT assets at any time.
How Panorays Helps You Manage Third-Party Risk
Panorays delivers a contextualized approach to third-party risk. It is the only third-party cyber risk management platform that measures risk uniquely, according to each business relationship.
Its modules include:
- Supply chain discovering and mapping. Reveal Shadow IT and hidden third, fourth, and n-th party vendors and map new breaches and vulnerabilities to them, so that you can each according to their criticality.
- Risk DNA Assessment. Combine internal and external assessments to deliver evolving customized risk-based ratings for comprehensive and accurate Cyber Postures assessment. Internal assessments include dynamic and customized questionnaires according to your risk tolerance and vendor profiling. External assessments include mapping and identifying third-party digital assets for vulnerabilities, control failures, human risk, AI dependencies, and past breaches.
- Continuous threat detection. Get early indications of breaches and vulnerabilities, prioritized according to the criticality of your third party. With a contextualized view of your supply chain, you’ll discover critical findings that deliver risk insights and alerts to prioritize threats and prevent them from escalating.
- Remediation and collaboration. In the event of a data breach or security incident, you’ll be able to see which vendors have been impacted and respond with an automated and collaborative approach between your organization and the relevant third parties.
Want to learn more about how Panorays can help you manage your third-party risk? Get a demo today!