Artificial Intelligence (AI) is top of mind for enterprise leaders across every business sector and tech giants like Google, OpenAI, and Amazon are placing big bets on AI’s future, investing billions in what they see as a huge upside for businesses using AI to drive efficiencies, improve customer service, and generate future profits.
What’s keeping CISO’s up at night, however, is not AI’s vast potential but how to harness its power in a responsible way that ensures data privacy and safeguards against a company’s intellectual property being usurped by an employee who mistakenly shares proprietary data through an AI tool or a third-party vendor that gets breached.
AI Is Awesome!
No one can deny that AI is an amazing technological breakthrough and its use across every business sector grows seemingly by the hour.
As the National Health Institute points out, AI has been incredibly helpful in cancer research and will no doubt have applications that will extend to many other areas of healthcare going forward. “AI and ML have demonstrated greater accuracy in predicting cancer than clinicians. These technologies also have the potential to improve the diagnosis, prognosis, and quality of life of patients with various illnesses, not just cancer.”
Financial institutions also see huge profit opportunities driven by AI, particularly in the corporate and retail sectors. A McKinsey Global Institute estimate cited recently that, “among industries globally, gen AI could add the equivalent of $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion annually in value across the 63 use cases it analyzed. Among industry sectors, banking is expected to have one of the largest opportunities: an annual potential of $200 billion to $340 billion (equivalent to 9 to 15 percent of operating profits), largely from increased productivity.”
Even restaurants and grocery stores have joined the AI stampede (yes, AI is checking on dumpsters to track how much food we waste).
All of these applications offer terrific benefits, but what does the flip side of AI look like if it’s not used responsibly? And, more importantly, how can CISOs control its use to ensure valuable data is safeguarded?
What Are the Risks if AI Is Misused?
Trying to pin down the risks associated with using AI either within your own company or with third parties with whom you’re doing business is a huge challenge, but the process needs to start by understanding:
- How AI is being used?
- Who is using it?
- What kind of attack-surface-management process is in place (if any)?
As Demi Ben-Ari, Co-Founder & CTO, Head of Security a Panorays explains, to understand the risks associated with AI, companies need to do reconnaissance on their own infrastructure, just like hackers would. Done properly, such an audit will reveal which third parties are using AI. And remember, third parties aren’t just vendors. They could be a business partner in any number of use cases (including software companies like Microsoft) that you might be using within your organization. It could even be a third party that is monitoring subsidiary companies for you globally just as Bloomberg does.
Problems arise, however, when companies using AI tools begin sharing information. For example, ChatGPT is problematic for companies because, without the proper technology, there is no way to monitor what kinds of information an employee might be typing into its search engine.
Are they inputting harmless data or are they sharing valuable IP or customer data that can open the door to huge privacy problems? As Ben-Ari notes, “You’re basically giving [ChatGPT] your data, and it’s a total black box. As a CISO, you have no idea what’s happening there.
To complicate matters further, AI is constantly “learning” and evolving, so if you’re using a third-party service that employs an AI engine, that use case is ever-changing and could leave your company vulnerable to information leakage or a hack. Ben-Ari says we need to “think of AI as an underlayer or the vendor of your vendor.” But how do you identify which vendor is using AI capabilities that you should be worried about?
The Challenges
As Ben-Ari sees it, the challenges CISO’s face today can be broken down into five key areas:
- Data Transfer: This is a biggie. Transferring data runs the risk of violating data privacy (think of our bank example where customer data might be shared unintendedly), but there is an even bigger problem in who is actually retrieving that data? Again, you’re pouring information into a black box over which you have no control.
- Data Regulations and the contradictions they pose: Right now there are two streams of regulations coming in from the US and EU in parallel. The problem is that the regulations contradict what actually happens when AI is used to process data. As Ben-Ari explains, “They [the regulations] actually state that an individual can come and ask what type of data a company is processing of theirs. They can ask to delete the data or retrieve the data. If you took a piece of data and processed it inside an AI model, however, practically speaking it’s lost or merged into the model…so it contradicts.”
- Challenge of the unknown: In the next few years, new AI applications will no doubt emerge. CISO’s will want to adopt them, but again, there’s a big question about what kind of risk exposure you’re subjecting your company to when you adopt these new technologies.
- Offensive AI: While AI is being used for many good purposes, it’s also being used by criminals to hack into company databases. “So you can basically take AI applied to every aspect of cybersecurity today both for offensive and defensive use,” Ben-Ari said. This is why CISOs need to understand what’s happening right now.5.Data Skewing: This is when someone tries to trick the AI model by feeding alternative data into it that “skews” the outcome, which could be disastrous for a company that is relying on AI-driven data to run their business.

So, how are CISO’s supposed to conduct the proper process of actually mapping out all of the AI capabilities and scoping out the risks to ensure their data remains secure?
Managing AI-Driven Risks
With suppliers and their subcontractors adopting AI in an undisclosed and potentially risky way, the potential for third-party data leaks and supply-chain attacks increases. Many organizations lack visibility into the 4th-to-Nth-degree subcontractors for their partners and suppliers, and can’t assess the security maturity of these organizations.
CISOs need to take the lead in defining their organization’s acceptable use, governance, and risk-management policies to securely implement AI technologies. This includes identifying risks, assessing AI tools and vendors for the strength of their controls for these risks, and monitoring and managing vulnerabilities throughout the implementation and usage of AI systems.
Here’s a practical guide that every CISO can follow to scope out AI-driven risks in their supply chain and provide safeguards around using this technology:
1. Detection
Enterprises need to start by identifying which third-parties in their supply chain are using AI.
- Inventory all third parties, marking those known to use AI
- Leverage technology to identify suppliers who don’t reveal AI usage
2. Profiling
Map the AI-based third party by their criticality, sensitivity, and risk markers. These include:
- Degree of human interaction
- Direct or indirect impact on humans
- Sensitivity of training dataset
- Sensitivity of “prompts”
3. Governance
Verify general security and privacy controls, as well as AI-specific controls by using questionnaires that ask:
- Is the use of testing and training data in compliance with privacy laws?
- Are there limitations in place to access sensitive data and “outcomes”?
- Are there oversight processes to detect unwanted model behavior?
- Are inputs validated to block anything adversarial?
- Is output monitored to flag large variations in model behavior and detect changes to training data not connected with a planned enhancement or entered by unauthorized users?
Controls for AI systems also need to be implemented internally:
- Educate users in the responsible use of the AI application
- Teach how the model should work and what level of accuracy is expected
- Ensure logging of AI application usage, inputs, outputs, and changes in user privileges
4. Continuous monitoring
Mitigating risk is not a one-and-done exercise because the threat landscape is constantly evolving. Enterprises need to constantly assess threats to stay ahead of potential breaches.
A Total Solution for AI Security
Panorays’ third-party cyber risk management platform (TPCRM) provides a complete, end-to-end solution to securely implement AI technology at your company by:
- Providing visibility into your vendor’s security controls, as well as reveal their technology relationships.
- Mapping new vulnerabilities and breaches to your digital supply chain, enabling you to act against potential threats, including those associated with your AI technology.
Panorays uses a highly sophisticated engagement system that provides detailed information through questionnaires that can be customized and rolled out in a series to probe more deeply into an organization’s third-party risk exposure to provide:
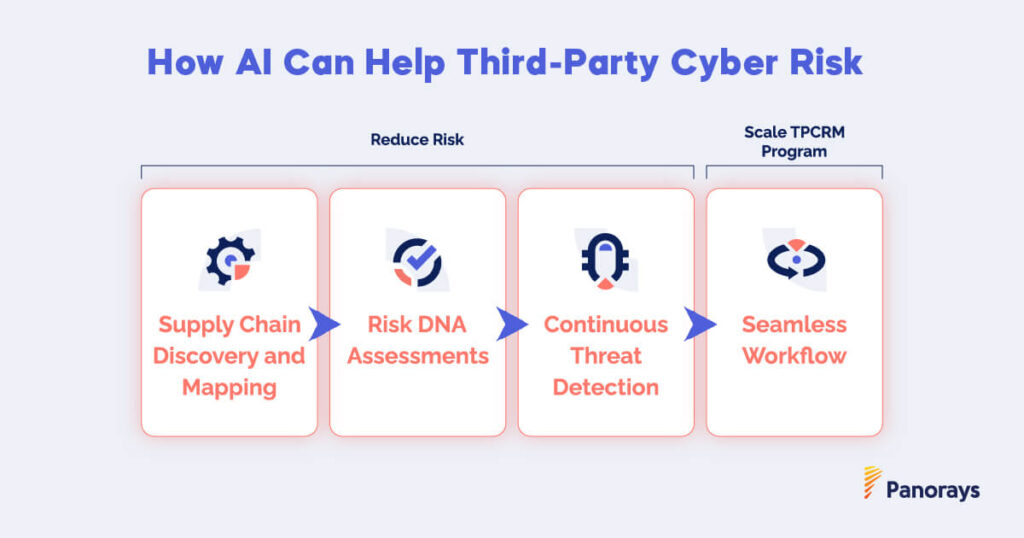
Supply Chain Discovery and Mapping
- Identify the parties – 4th-Nth parties can be identified through a variety of AI-driven techniques, enabling supply chain discovery and threat mapping.
- Automated risk profiling – AI technologies can automatically identify your third and fourth parties’ basic information; risk tiering them according to business function.
Risk DNA Assessments
- Accurate asset discovery – Machine learning “affiliation” models can identify digital assets of third parties and their respective supply chains, minimizing false positives.
- Breach prediction – AI models based on historical datasets can indicate the likelihood a supplier may be breached.
Continuous Threat Detection
- Contextual threat intelligence – Leverage AI-driven parsing and named-entity recognition to map threat feeds to third parties and their supply chains.
- Enhanced Visibility/Prioritizing – Classify cyber-threats according to third-party business context to limit the cyber-threats report to those relevant to your company.
Seamless Workflow
Scale the questionnaire process with powerful automation to provide:
- Accelerated evaluations – AI NLP (natural language processing) technology can help third parties answer questionnaires faster by selecting relevant answers from previous responses.
- Zero interaction assessment – NLP parsing of uploaded documents and publicly available information can autofill a new questionnaire.
- Efficient validation – AI technology can map document sections to questionnaire responses, speeding validation.
Ben-Ari revealed in a recent podcast that AI is incredible, but “it’s frightening to know all the things we don’t know about AI.” CISOs can take comfort, however, knowing they have solutions at their fingertips that can quickly size up the risks from those using AI in their supply chain to ensure their most-valued data remains secure.
To see how Panorays can help manage third-party AI risk in your digital supply chain, click here.



