A recent study conducted found that data breaches cost nearly $4.45 million globally and that number will only increase as attack surfaces increase, data volumes rise and IT environments grow more complex. One of the methods organizations should have internally and also ensure are in place with their third parties to defend against these data breaches is data protection.
What is Data Protection?
Data protection is the process of ensuring that sensitive information and records are safe from unauthorized use. When in the hands of unauthorized users, sensitive and private data could be leveraged for malicious intent, such as ransomware attacks, stolen to sell on dark web marketplaces, or leveraged by cybercriminals to execute identity theft or even pose risks to national security.
Why is Data Protection Important for Third-Party Risk Management?
Not only is data protection a requirement for all businesses, but it is also a requirement for any third parties they rely on that integrate into their IT infrastructure.
The benefits of proper data protection include:
- Minimize the risk of data breaches and supply chain attacks. If data protection measures such as proper access controls, encryption and MFA are in place, it makes it more difficult for cybercriminals to access the data, even via third parties, and use it for malicious intent.
- Avoid regulatory fines and litigations. Adherence to regulations, such as GDPR, PCI DSS, HIPAA and CCPA helps businesses avoid hefty penalties for a violation of data protection practices either internally or through a third party.
- Strengthen your cybersecurity posture and operational resilience. Having a strong data protection policy in place also ensures that your business and third parties have a plan for business continuity in the event of a data breach or security incident.
- Build greater trust in your business. Businesses prefer to enter into relationships with third parties who have a strong data protection plan in place. This in turn builds customer relationships who value your commitment to security.
Data Protection vs Data Privacy
| Data Privacy | Data Protection | |
| Definition | Proper handling of personal data, such as PII and PHI | Enabling sensitive data for only authorized use and defend against cybersecurity threats |
| Domain | Legal | Technical |
| Process to achieve it | Controls on gathering data set by individuals | Controls and frameworks set by a business |
Data Protection: A Focus on Technical Controls
Data protection is the safeguarding of sensitive or confidential data from unauthorized use by hackers or even insider threats. Controls and frameworks are applied with the goal of protecting data from cyberattacks and data breaches. In 2023, debt collection agency EOS Matrix was hit by a fine of $5.8 million after Croatia’s data protection regulator was found to have illegally processed the data of its individuals with outstanding debts with credit institutions.
Data Privacy: A Legal Matter
Data privacy, on the other hand, involves the policies or regulations used to ensure only authorized use of sensitive or confidential data. When data is protected under data privacy laws, for example, consumers are entitled to sue a business in the event of a data breach. Failure to protect data privacy can result in massive fines, such as the $1.3 billion fine Meta was ordered to pay for violating EU data privacy laws stipulated in the General Data Protection Regulation.
What are the Main Third-Party Data Protection Regulations?
Since businesses enter into relationships that require them to share customer data with third parties, it’s important that both parties adhere to various regulations and standards concerning both data protection
These include:
- HITRUST. HITRUST, the Health Information Trust Alliance, offers a comprehensive framework for third parties that combines different federal regulations and standards and alignment with third-party vendors, including data protection and privacy policies outlined in GDPR, to meet compliance and security standards. Third-party vendors with HITRUST certification signal to healthcare organizations that they have a strong security policy in place to safeguard PHI data.
- ISO 27001/27799. ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized security standard that helps organizations improve their information security management systems (ISMS). It includes components related to risk management, access control and adherence to compliance related to data privacy and protection. As it is the only standard of the ISO series that can be audited and certified, it is an indication of an ongoing commitment to maintaining and improving these security systems. ISO 27799 extends the standard to the healthcare industry.
The Top 4 Data Protection Challenges for TPRM
With ransomware demands of up to $5 million from Snowflake customers and terabytes of data breaches stolen from TicketMaster and Santander, it is more apparent than ever that effective data protection is essential not only for your organization but also for your third parties. But even with this realization, both organizations and their third parties face a number of challenges in implementation.
These include:
1. An evolving threat landscape
CISOs and security teams are faced with aiming at a moving target when it comes to cybersecurity. The increase in IoT, third party integration and cloud migration have expanded the potential attack surface for cybercriminals to exploit. Supply chains have become more complex, requiring advanced third-party management, and supply chain attacks such as SolarWinds have demonstrated their ability to impact thousands of global organizations, from the U.S Department of Homeland Security and U.S. Department of Defense to Intel and Microsoft. At the same time, the dynamic nature of networks and IT infrastructure require continuous monitoring to ensure effective defense against cybersecurity threats.
2. Increased reliance on third-parties
Many enterprise-level organizations, especially those in the financial industry, for example, have multiple top-tier cybersecurity solutions in place to defend them in the event of an attack. Cybercriminals know this, however, and intentionally try to infiltrate your network and systems through third parties, who often have smaller budgets for those same cybersecurity solutions or implement employee awareness training. Since the average enterprise-level today relies on an average of 88 third parties, there is no shortage of opportunities for cybercriminals to exploit.
3. Accelerating regulations and standards
Compliance continues to evolve, with new regulations and standards being put into place all the time. Organizations must adhere to the relevant regulations of their industry, which are evolving rapidly to include technological changes such as artificial intelligence and the increased risk posed by outsourcing to third parties. For example, the AI Act is a European regulation and one of the first to impose limitations on the use of AI technology. DORA, NYDFS and the NIS2 Directive provide guidelines to organizations on how they can best deal with the risks posed by sharing data with third parties.
4. Increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI)
While AI offers more opportunities for organizations to scale their third-party risk management and improve the accuracy of risk assessments, it also poses risks. These include data privacy and control issues, such as the leaking of personal information of customers, source code and intellectual property (IP) used to train AI models. Prompt engineering can direct AI to act maliciously and polymorphic attacks can deliver customized and convincing phishing attacks at scale. AI technology also expands the attack surface and the risks posed by third, fourth and n-th level parties.
5 Data Protection Best Practices
Organizations who want to strengthen their data protection must employ a robust approach that combines technology, policy and human factors to effectively manage their data assets.
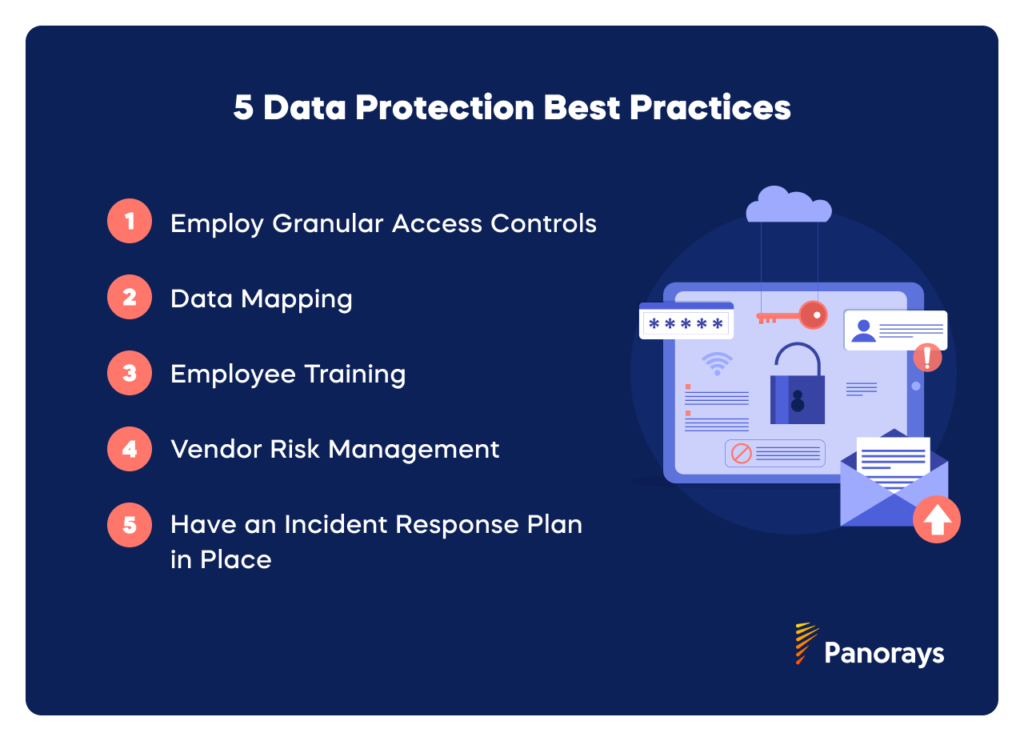
Employ Granular Access Controls
Strengthening access controls to include granular access controls such as role-based access controls and the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) is one of the best strategies for protecting customer data not only within your organization but data accessed by your third parties. PoLP in particular operates on the idea of zero trust, which goes beyond ensuring initial authorized network access by continuously re-evaluating and re-authenticating access. Effective third-party risk management means that an organization implements zero trust architecture internally yet also ensures that its third parties also have a properly functioning zero trust architecture.
Data Mapping
A requirement under GDPR (e.g., an Article 30 assessment) and also known as a personally identifiable information disclosure under CCPA, data mapping explains where and how your organization handles customer data. As more regulations evolve and companies rely increasingly on third parties, organizations need tools that enable them to automate and scale their data mapping.
Vendor Risk Management
Vendor risk management is a strategy designed to limit the number of threats, vulnerabilities and weaknesses your business faces from your business relationships. Proper vendor risk management evaluates these threats throughout the entire vendor lifecycle, not only during the vendor relationship, but also during onboarding and offboarding as well. An effective vendor risk management program sends cybersecurity questionnaires and risk assessments to third-party vendors regularly to continuously assess vendor risk based on predetermined criteria.
Have an Incident Response Plan in Place
Businesses can effectively mitigate attacks by having a detailed plan in the face of an attack. Although managers in IT and security teams may take the lead in this situation, everyone in your organization should be aware of their role. This should also include a list of which authorities should be reported and the timeframe for reporting according to different regulations. Incident response plans also include data backup and an effective data recovery program so that business operations can continue in the event of a data breach or security incident.
Employee Training
Almost three quarters (75%) of data breaches are the result of a human error, whether it’s due to privilege misuse, weak passwords that allow cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities or falling for a sophisticated social engineering or business email compromise (BEC) attack. For example, employees must be made aware of the latest phishing attacks relevant to their specific titles, strong password best practices and their role in the event of a cybersecurity attack. Employee training is a central tenant in building a culture of security awareness within your company.
How Panorays Helps You Manage Third-Party Risk
Panorays offers a contextualized approach to third-party risk to help strengthen data protection both within your organization and across third, fourth and n-th parties.
Its modules include:
- Supply Chain Discovery. Automatically discover unknown third, fourth, and n-th parties in your supply chain and define the relationship between your organization and each third party so that you have a better understanding of how data is shared between the different parties.
- Risk DNA Assessments. Conduct both internal and external assessments of your third parties and determine each supplier’s risk appetite. Risk DNA also takes into account all third-party breach history and generates AI-driven predictions for future data breaches. All of these elements work together to deliver the most accurate cyber risk rating of your third parties on the market today.
- Continuous Threat Detection. Leverage third-party threat intelligence and a contextualized view of your supply chain to get alerts of any relevant data breaches or supply chain attacks from third parties.
- Remediation and Collaboration. Close supplier gaps immediately with an aggregated remediation plan for each vendor. Each plan takes into consideration your risk appetite, critical findings and potential business impact of each risk.
Want to learn more about how Panorays can help you manage third-party risk and strengthen your data protection? Get a demo today!