Third Party Risk Management (TPRM) is the process of managing risks with third parties that are integrated into your business IT infrastructure and an essential cybersecurity practice for businesses today.
At the beginning of 2024, the headlines already started announcing third party data breaches. This time it was Fallon Ambulance Services, a Boston-area service acquired by Transformative Healthcare more than six years ago. The breach occurred when malicious actors gained unauthorized access to archived files in the ambulance service’s data storage. Transformative Services announced that the personal and medical data of nearly a million customers was exposed, including social security numbers, vaccination information and employment information from applicants who had displayed interest in working with the ambulance service.
With stories of third party breaches being reported in the news among even the most leading organizations and brands, CISOs and security teams are looking more at third party risk management to step up their security.
But how exactly does third party risk management (TPRM) work, and why is it so crucial for a strong cybersecurity strategy?
What is Third Party Risk Management (TPRM)?
Third party risk management (TPRM) is the process an organization implements to manage risks that are a result of business relationships with third parties that are integrated into their IT environment and infrastructure. These risks can be operational, cybersecurity, regulatory, financial and reputational. According to a survey from Cyber Risk Alliance, the average organization uses 88 IT third parties (including software and service providers, partners, external contractors, agencies, suppliers and vendors), and larger organizations can rely on nearly twice as many (175) third parties.
The Most Common Third Party Cyber Risks
Risk management technology can help your organization both consolidate vendor information and conduct an ongoing third party risk assessment of all your vendors to help identify risk factors and evaluate each vendor’s inherent risk. Often, the technology determines the risk according to risk scores. After identifying the risk level that each vendor poses, a risk reduction strategy can be put into place according to your organization’s risk tolerance.

Third party risks include:
- Cybersecurity risk. A data breach, phishing, DDoS, social engineering or ransomware attack from a third party can cost your organization in time and resources, halt or disrupt operations and significantly impact its reputation.
- Operational risk. If a third party provides a critical component of your system and is disrupted due to a natural disaster, political conflict or cybersecurity attack, it also poses a critical risk to your business continuity.
- Financial risk. If a supply chain is poorly managed, it can result in financial risk to a third party as they are unable to properly evaluate which products they offer are in high demand and which are not.
- Strategic risk. Market changes, new acquisitions or mergers, and changing expectations of customers can make it difficult for all parties in the supply chain to align on business strategy.
- Compliance risk. Compliance requirements depend on the industry (e.g. HIPAA and PCI DSS), your company’s location, and your customer’s location (e.g. GDPA, CCPA, EBA).
- Geopolitical risk. For example, political tensions can make it difficult to continue a business relationship with a supplier or vendor. Political instability can motivate companies to look for a vendor in another location.
Who is Responsible for TPRM?
Traditionally, TPRM has been the responsibility of the procurement or risk and compliance teams. For example, at one time a banking system had limited interaction with third parties. Perhaps a consultant would come in to evaluate specific programs or procedures, or a lawyer might examine internal processes to determine any legal risk. Integration was limited to networks such as SWIFT, an international system for exchanging monetary transactions, which would integrate into the banking system. As software systems become more interdependent, however, each bank evolved into a complex layer of third, fourth and even fifth-party systems.
As a result, a dedicated third party risk professional today is an essential part of the third party risk management process, particularly in the banking and finance industries. This person is responsible for assessing and managing the third party risks for an organization, which includes a wide range of responsibilities such as collecting information from third parties, assessing their ability to manage compliance, prioritizing third party risks, creating and sending questionnaires to these third parties, and overseeing legal contracts such as SLAs to mitigate any legal risks to the organization.
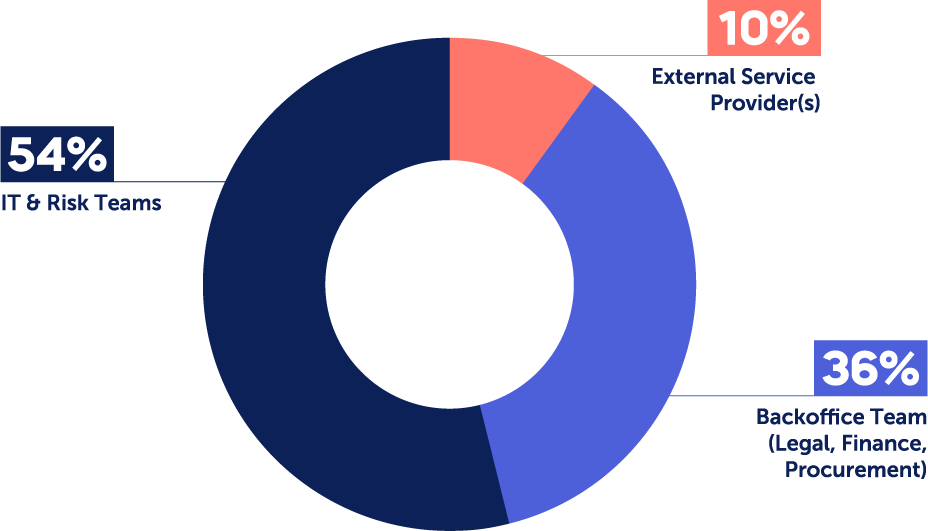
A recent Panorays survey found that:
- In more than half of cases (54%), the responsibility for third party cyber risk management falls under dedicated IT and Risk teams who have specific technology expertise. These include Operations and Logistics teams, Compliance and Privacy, Information Security, Risk Management, and Technology or IT.
- In 36% of cases, the Back Office Team is in charge, which includes Legal, Finance and Procurement. This may include tasks like managing cyber questionnaires, onboarding third parties to internal systems, or handling payments.
- While 10% outsource third party cyber risk management to external service providers, this is predominantly the case in enterprises with under 5k employees.
What We Saw in TPRM in 2023
Let’s take a quick look at a few of the trends we saw this past year.
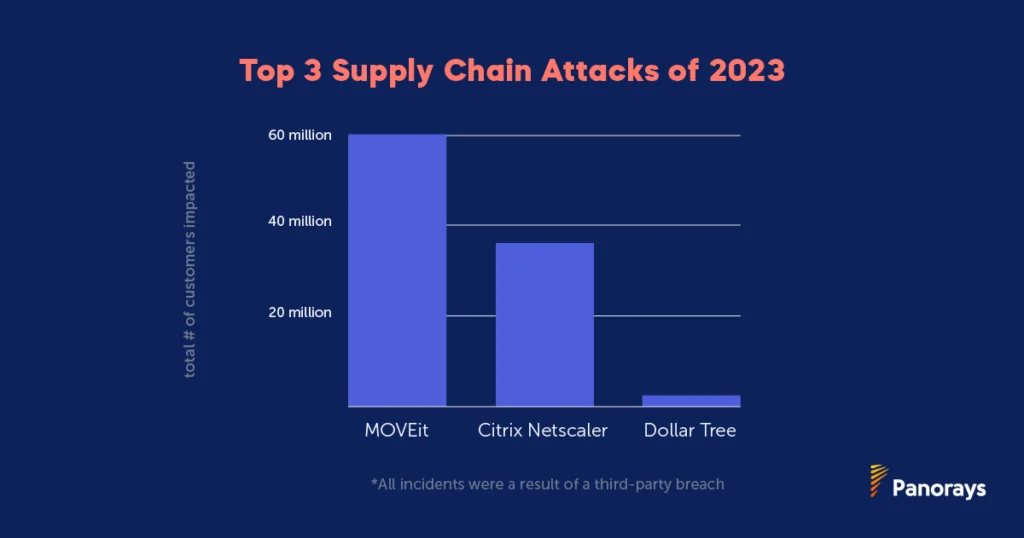
- An increase in supply chain attacks and third party breaches. We continued to see major digital supply chain attacks such as MOOVEit and Citrix Netscaler and third party breaches such as Okta and Dollar Tree. Both of these types of attacks emphasized the need for greater visibility not only of their third party ecosystem but identifying and mapping fourth, fifth and n-th parties as well.
- Third parties continue to offer cybercriminals more opportunity for attacks. Enterprise-level companies often have the budget and resources to spend on cybersecurity solutions aimed at mitigating low-cost and common phishing, email security, social engineering and Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks. Advanced TPRM platforms, however, are necessary to defend against attacks on third parties that may not have these types of security systems in place.
- Understanding the criticality of your third parties is essential. As supply chains increase in complexity and the number of third party risks increase, organizations must determine the importance of each vendor to their business and the sensitivity of data shared with them. They can then monitor them regularly and communicate with the third party at the head of the supply chain to remediate these threats or vulnerabilities as they are identified.
Trends in TPRM We Should Expect to See in 2024
Now that we’ve reviewed the trends in TPRM of the past year, what are the TPRM security risks we should be aware of in 2024? Here are a few of the trends that third party risk and security teams will need to stay on top of and learn to communicate how impacts the company’s business goals.
1. Increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI)
We will witness artificial intelligence continue to be a double-edged sword in terms of security in 2024. On the one hand, AI-powered third party risk platforms can assist in enabling organizations to scale their third party management by improving the accuracy of risk assessments. For example, it can accelerate the process of completing and evaluating cybersecurity questionnaires through AI-generated answers based on past similar questionnaires and AI-powered validation of answers by cross-referencing them with vendor documents. It can also use AI to map the digital supply chain and identify the KEVs, CEVs and vulnerabilities relevant to each party so that organizations can prioritize and remediate against risk more efficiently.
At the same time, however, AI poses continued risks to security risks to organizations when used by an organization’s third party.
These risks include:
- Data privacy and control. Training models based on personal information of customers, source code and intellectual property (IP) information risks being leaked. Biased data samples, misinformation and “hallucinations” result in inaccurate responses that hurt an organization’s reputation and damage user trust. Forrester predicts that in 2024, a third party application will be fined for compromising the personal data of its customers. Companies integrating these third party applications should consider how their combined lack of resources and knowledge of mitigating risks make them attractive targets to attackers.
- Security. Polymorphic attacks can be used to send convincing, well-written phishing emails to customers at scale, changing the text just enough to evade phishing detectors. Other techniques such as prompt engineering and indirect injection from training data direct an AI to act maliciously. For example, users can create prompts that direct AI to reveal sensitive information and generate misinformation or code that can be used to launch a cyberattack. Indirect injection from training data can embed malicious instructions or data from sources the AI ingests or insert malicious content into the training data itself.
- Supply chain risks. As suppliers adapt AI too, often even faster than your organization, attack surfaces expand without being aware of the third, fourth, fifth and n-th parties in the expanded digital supply chain, the risks they pose and the level of criticality each business relationship has with your organization. This makes it increasingly challenging to meet compliance and regulations that are related to third party risk management.
2. Emphasis on cloud-first strategies
As companies rush to increase the digital transformation of their businesses and their attack surface increases, they lose the control they used to have when these applications were on-premise. This is particularly true with regard to their data security. Many cloud infrastructure systems, such as AWS, operate on a shared responsibility model. Amazon takes responsibility for the physical security of their infrastructure, but the responsibility for software updates, configurations and data security remains in the hands of the SaaS providers hosting on AWS. When a company outsources a service to a SaaS payment service, for example, and that payment service uses a cloud provider such as AWS to host your company’s data, the company can’t make any assumptions about the security practices the SaaS service has in place to protect itself against data breaches or other types of attacks.
Take the case of the Uber breach in 2015, which exposed the names and driver’s license numbers of 50,000 Uber drivers from its third party, Github. The breach occurred because a user was able to access the GitHub password and user credentials stored on the public application due to a misconfiguration of the AWS bundle, a security setting of the hosting package. In other words, Uber was responsible for its data security, but the data was hosted on AWS through its third party, Github, which it relied on to configure properly. Although best practices controls such as the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) Access and separations of networks can help form effective kill chains to defend against these types of attacks, mistakes still can and do occur.
3. Increased regulatory focus on the cyber risks posed by outsourcing to third parties
As a result of increasing reliance on AI and migration to cloud services, organizations must embrace accelerated governance while at the same time accepting greater accountability. In the past few years, global regulators have begun drafting complex regulations that specifically deal with the security risks posed by outsourcing to third parties.
These include:
- DORA. The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) was developed with the goal of regulating financial institutions in the EU to improve their cybersecurity resilience. This includes adopting Information and Communications Technology (ICT) security provisions such as mapping of third party assets, evaluation of third party criticality, and having a mitigation and remediation plan to deal with vulnerabilities as they occur.
- NYDFS. The New York Department of Financial Services (NFDFS) regulation is aimed at protecting the non-public sensitive information of financial institutions that conduct business with New Yorkers. It specifies guidelines for ensuring that data shared with third parties remains secure, including periodic risk assessments, the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA), encryption, and notification of any cyber incidents or data leaks.
- NIS2 Directive. This EU regulation includes a broader scope of organizations and industries than DORA. It outlines the types of security incidents that should be reported, including unauthorized access to services, data breach and DDoS attacks. It also emphasizes the importance of proactive risk management, including third party and digital supply chain risk assessments.
In 2024, we will see standards and regulations related to TPRM accelerate. AI-related regulation has only just started to develop, however.
This past year we saw:
- AI Act. The European regulations are the first to pose limits on AI technology, banning the use of certain applications such as facial in general and emotion recognition at work or at school. It also holds companies responsible for any damage incurred by the new technology.
- Executive Order on AI. These guidelines aim to protect U.S. citizens against the risks of AI by requiring greater transparency on how the models work and establish a new set of standards. The overarching goal is to facilitate greater safety and security while encouraging its responsible and ethical use.
The Benefits of Third Party Risk Management
You can conduct third party security risk management using an internal team, or by working with a third party security risk management specialist. Either way, you’ll need to spend time and money and implement new business processes to improve your risk profile. Either way, investing in third party security risk management offers a number of benefits.
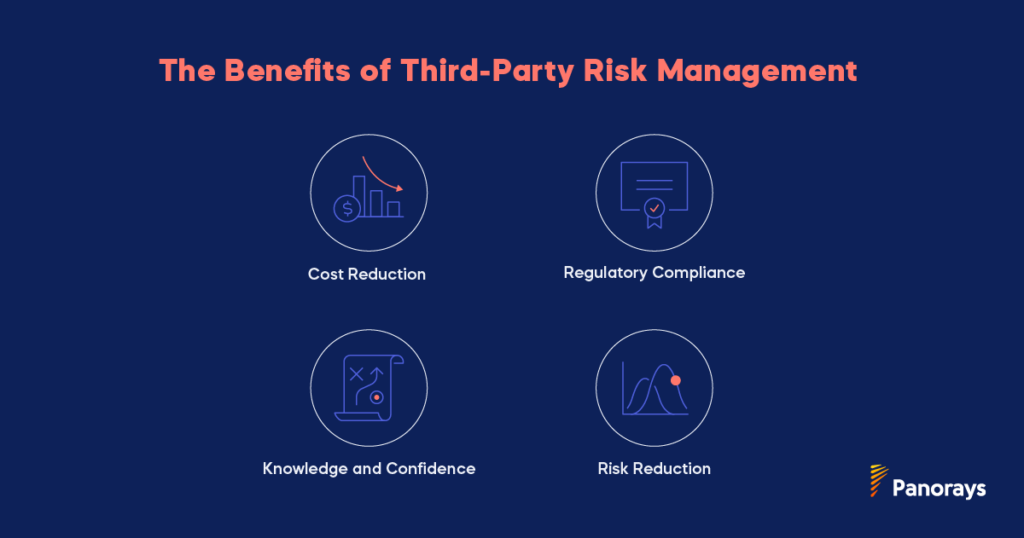
They include:
- Cost reduction. First, it’s appropriate to think of a third party risk management program as an investment. Even though it will cost you some time and money upfront, it stands to save you money in the long run. A data breach could cost your company thousands if not millions of dollars – but an effective third party cybersecurity risk management strategy could prevent you from ever facing this scenario.
- Regulatory compliance. Second, you are legally required to meet industry regulations that include components of TPRM. Whether or not you implement TPRM directly or outsource it to an external party, however, you are still bound by these regulations. This is particularly true for industries that deal with customer data.
- Knowledge and confidence. Third party risk management also increases your knowledge and visibility of the third party vendors with whom you’re working. The more confident you are in your network of vendors and partners, the more seamlessly you’ll be able to work.
- Risk reduction. Continuous third party risk management is instrumental in order to tier your third parties properly and gain better insight into risk posed by fourth parties. When new vulnerabilities and data breaches are discovered, you’ll have the context to prioritize them effectively.
Why CISOs are Choosing to Invest in TPRM
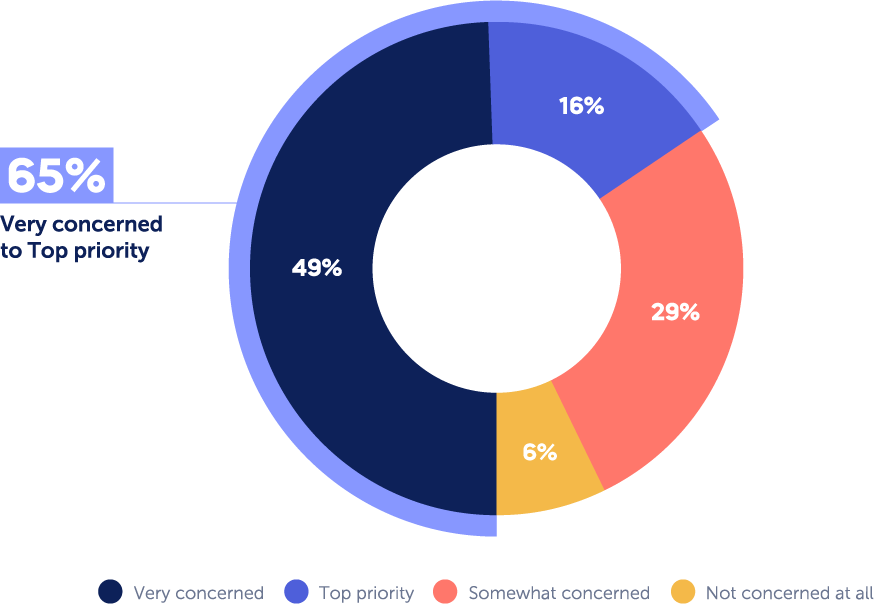
A recent survey conducted by Panorays found that the vast majority – 94% of CISOs are concerned about third party cybersecurity attacks; and 16% rate it as their top priority. The level of concern may depend on different factors, such as the size of the organization, how reliant it is on third parties for critical services, and the need for it to adhere to various regulations. As a basic rule of thumb, however, the larger the enterprise, the more concerned it is about third party attacks due to the potential risk and consequence of a third party breach.
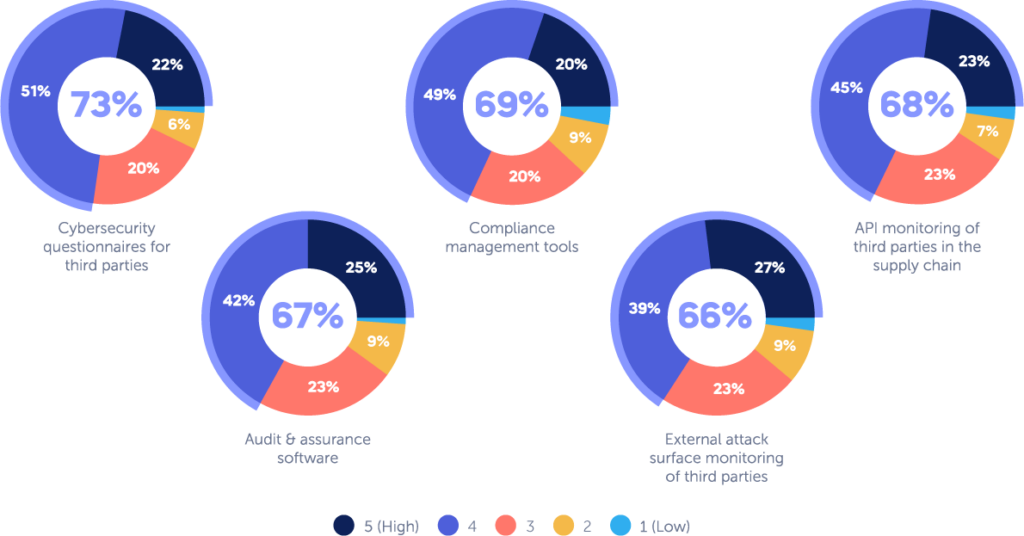
No Silver Bullet in Terms of Third Party Tools
CISOs also realize that when building a third party risk management program, combining multiple tools is the key to success. Although CISOs have slightly different opinions as to the effectiveness of different tools, they agree on the importance of a few main ones. Nearly 73% found cybersecurity questionnaires to be effective; 69% compliance management tools; 68% compliance management; 67% audit and assurance software and 66% external attack surface monitoring of third parties.
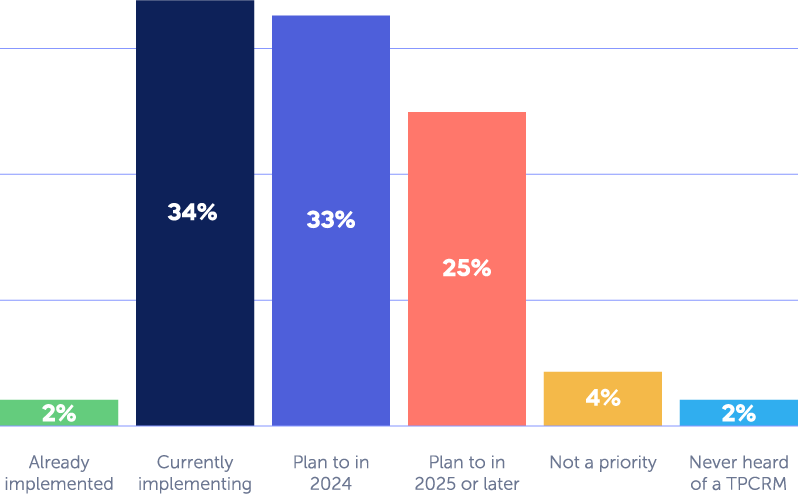
What to Consider When Selecting a TPRM Platform
According to a recent Panorays survey, 65% of CISOs have increased their budget for third party risk management and 92% of them are allocating these resources to implementing a designated solution for third party threats.
When considering a TPRM platform, there are a number of factors to consider such as:
- Scalability. With enterprise-level companies relying on as many as 175 third parties, it’s important for them to have minimal friction when dealing with suppliers to reduce time spent on security assessments and resolve issues quickly. Once you have identified your third parties, deploy a security questionnaire and an external cyber posture assessment so you can easily verify every third party’s security policy and posture. Automated and customized cybersecurity questionnaires help minimize this friction, with targeted questions that apply only to the specific third party and its relationship with you.
- Attack surface assessment. An external assessment can provide a picture of the third party’s exterior attack surface.You should perform regular third party risk assessments to identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities inherent within their IT and network, applications and human layer.
- Mapping of the supply chain. Many organizations aren’t even aware of how many third parties they use, much less the types of critical services they provide. Profile each vendor, grouping them with similar vendors. List what service they provide, the criticality of that service, the types of data they are handling, whether and how much they handle sensitive data and the internal contact managing the vendor. This will help you determine which questionnaires to send out to your vendors, according to your regulatory requirements and risk appetite.
- Continuous monitoring. Hackers are constantly using new and advanced methods to exploit new vulnerabilities and engage in cyberattacks. In addition, suppliers frequently add new assets and software and may also change or update their internal policies. All of these can result in new cyber gaps. With continuous monitoring, your organization can take a more proactive approach by uncovering issues, detecting suspicious activity and staying updated about security policy changes, with the data it receives in real time.
- Remediation. Remediation or mitigation plans should be provided to the third party, along with visibility about how cyber gaps were found. You should then set realistic deadlines and provide an intuitive method for communication. In short, you and your third party should establish a collaborative business relationship.
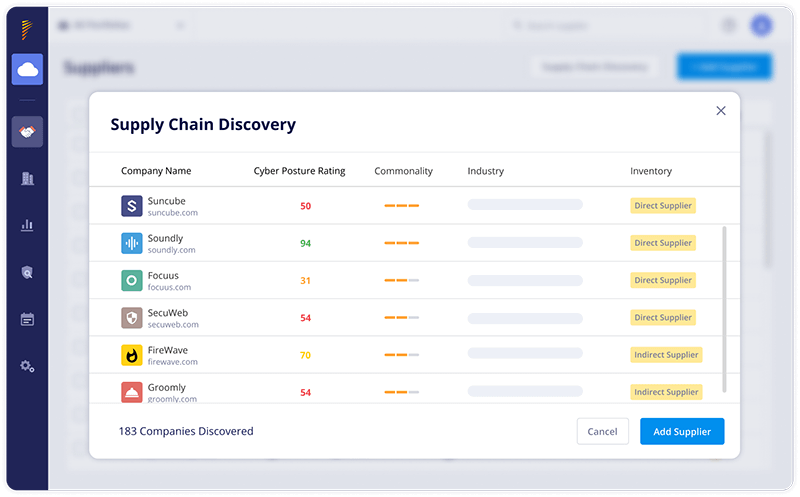
How Panorays Helps Manage Third Party Risks
Panorays is the only third party cyber management solution that delivers contextual third party risk management. By mapping your full threat landscape and continuously monitoring and reassessing the Risk DNA of each business connection, it pinpoints early threat indications within the unique business context of every relationship, enabling companies to adapt their defenses, minimize risk and proactively prevent the next breach from affecting their business.
Platform screenshot direction below:
The platform includes:
- AI-powered cybersecurity questionnaires. Unlike traditionally cumbersome security questionnaires that can take days or weeks to complete, these AI-powered cybersecurity questionnaires can be completed in minutes. On the supplier’s end, AI assists in generating answers based on questionnaires conducted in the past. On the evaluator’s end, AI assists in evaluating the accuracy of responses by validating them with internal documents from both the organization and vendor.
- Extended attack surface assessments. These assessments start with first identifying and mapping third, fourth, fifth and n-th party relationships, identifying risk and prioritizing it according to the level of criticality so that organizations gain deeper visibility into the digital supply chain.
- Risk DNA Assessments. Assess the cybersecurity posture of your third parties with AI-based accuracy, taking into account the dynamic nature of every relationship. Risk DNA evolves to reflect changes that impact your third party risk, including shifts in data access and severity, changes in their business criticality and developing vulnerabilities.
- Continuous monitoring. Conduct attack surface assessments and send vendors cybersecurity questionnaires when necessary, such as when a change is made in your organization or vendor’s IT infrastructure, or an announcement of a change in the industry’s regulations.
- Automatic discovery of third, fourth, and n-th party vendors. Organizations don’t always know which third party services and applications they are using (much less fourth and fifth parties). Attack surface assessments begin by mapping and identifying third, fourth and n-th party vendors to understand the business relationship between them and your organization. Then it ranks them according to their level of criticality.
- Evaluation of compliance. Verify whether or not your suppliers are meeting compliance and continuously monitor for new issues for meeting regulations and standards such as GDPR, NDFS and PCI DSS. Replace clunky spreadsheets with efficient frameworks to document process-oriented regulations such as the OCC and EBA.
- Customized remediation. After sending cybersecurity questionnaires and identifying cyber gaps that need to be addressed, vendors and organizations can collaborate together using a detailed plan to remediate any risk you deem necessary, customized according to each organization’s specific risk appetite.
Want to learn more about how you can manage third party risk across your extended attack surface? Get a demo today.
Third Party Risk Management FAQs
-
Third party risk management is a process designed to review third parties for their current security practices, their role in your organization, and their overall sustainability. It includes the controls put in place to minimize operational, financial, reputational, financial and cybersecurity risks posed to your organization.
-
The five steps essential to third party risk management are:
- Analysis. Identify the inherent risk of the relationship of the vendor and the level of due diligence to be performed.
- Engagement. Collaborates with the third party to remediate security gaps.
- Remediation. The vendor or third party fixes the security gap.
- Approval. Approved or rejected the third party based on your organization’s tolerance for risk.
- Ongoing Monitoring. Conduct continuous monitoring to detect any cyber gaps of the third party.
-
Third party frameworks are sets of controls used to manage relationships with third parties. An example is the NIST CF or the National Institute of Standards Cybersecurity Framework, a voluntary set of standards used by organizations across industries, of all sizes, to strengthen their cybersecurity programs.
-
Third party risk management is important because third party risks have increased as more organizations rely increasingly on third parties for their operations and business growth. Recent supply chain attacks such as the MoveIt and Applied Materials attacks have highlighted the need to apply resources to TPRM.
-
Third party cyber risk management focuses on cyber risks with capabilities such as threat intelligence, ongoing monitoring, breach remediation, etc and is catered towards CISO, third party risk management and security and compliance teams.
-
The difference between TPRM and TPCRM is that TPRM, or third party risk management, focuses on the full range of third party risks such as financial, legal, cyber, reputational, strategic, operational and geopolitical. TPCRM, or third party cyber risk management, focuses specifically on managing cyber risks.





